Haptic-AI Framework: Integrating Touch Into AI Systems
With Nvidia’s AI-powered robot “Blue”, Tesla’s Optimus, and Meta’s making their own humanoid robot, we see how these big tech companies are all investing in AI-specific hardware. These are indicators that signal a clear transition from software-only AI to physically embodied AI systems that will be physically present in our homes, workplace and public spaces.
If we’re going to co-exist with AI that share our physical spaces, we should be able to interact with them not just through text, voice, or images. We also want them to be able to perceive, understand, and respond to touch interactions, just like how we communicate with each other in our physical environment. Think about it, when we greet, we shake hands. We give a gentle pat on the back to show encouragement, and a hard slap when we are angry. Even though we might not be lining up to high-five or cuddle with robots, they should at least be able to recognize and understand the emotional meanings behind these touch gestures to be considered as emotionally intelligent.
The Haptic-AI Framework
I designed the Haptic-AI framework to provide a structured overview of how we can integrate touch into AI systems. The primary purpose of this framework is to identify the various components required for integrating touch in AI systems. I put this framework together after consolidating research across multiple disciplines, including affective computing, haptic technology, machine learning, human-computer interaction, human-robot interaction, human-AI interaction, neuroscience, and psychology.
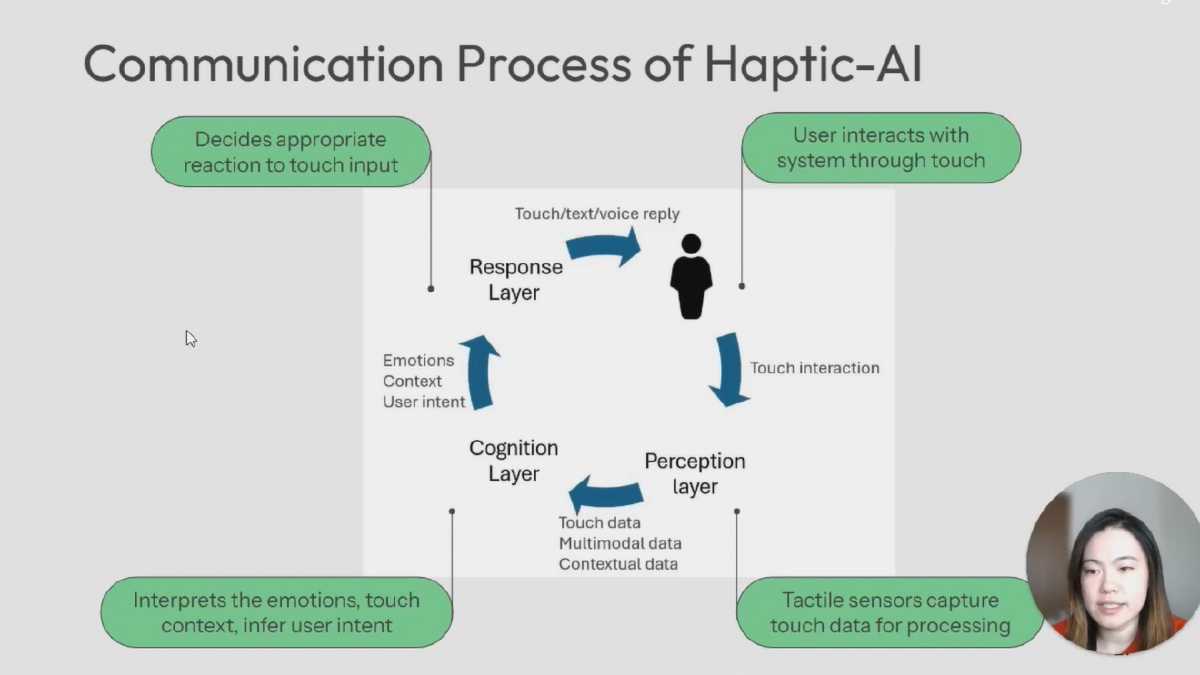
This is what I summarized into four core layers that work together to create AI systems capable of perceiving, understanding, and responding to touch.
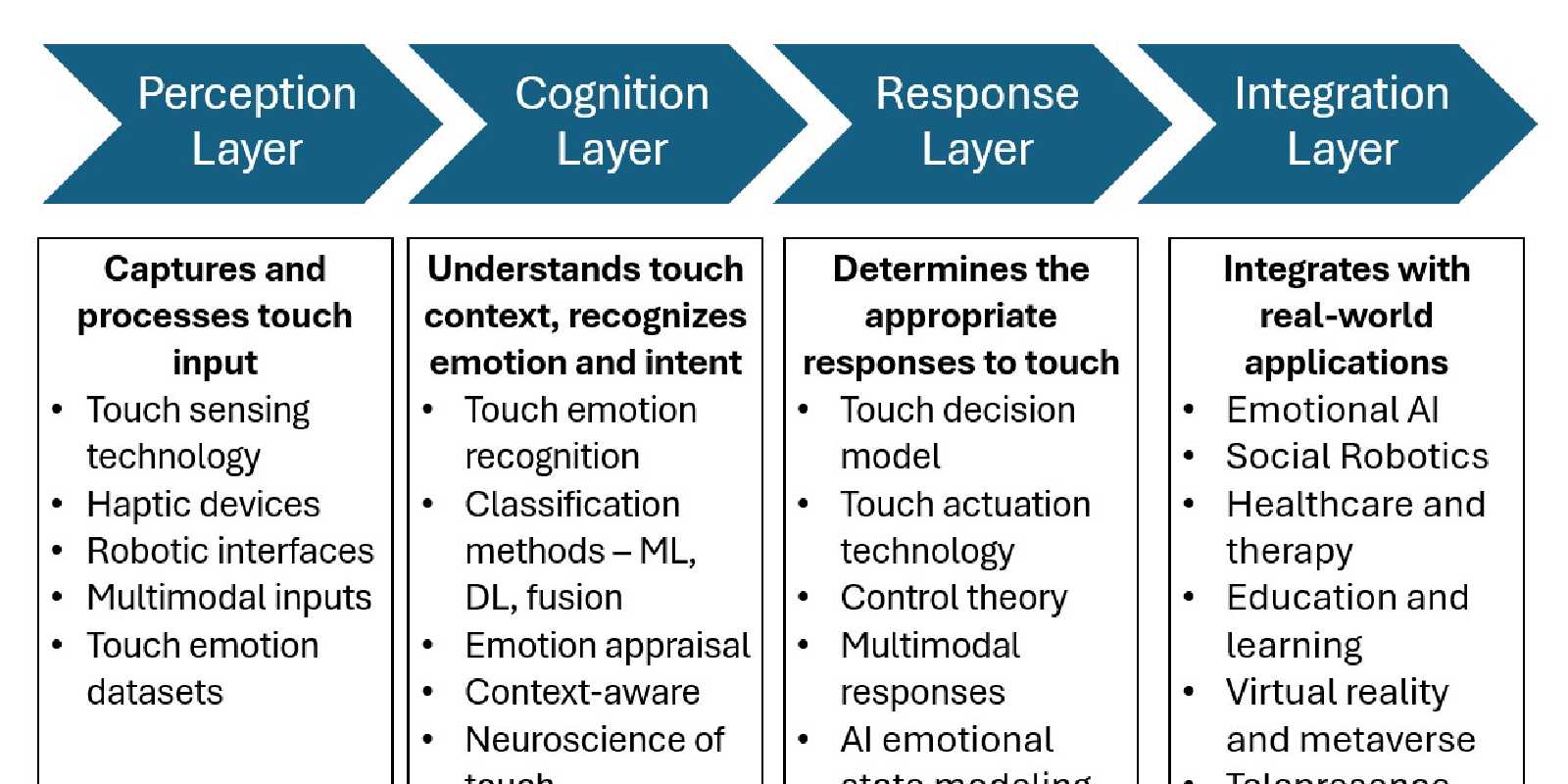
The Haptic-AI Framework
🔸 Perception Layer This is the sensory front line, capturing touch input with haptic-sensing interfaces. It can also be designed to integrate with other sensory data—vision, voice, text—to give AI a multi-dimensional understanding of what’s happening.
🔸 Cognition Layer This layer is the algorithm and AI models that analyzes the emotions and intent of the touch input within its social context. The cognition layer uses machine learning and deep learning methods to recognize emotions based on touch data. Touch-emotion datasets should be collected from real-world situations and used to train these emotion recognition models.
🔸 Response Layer Once the system understands the user’s emotions and intent, it needs to decide how to react. This layer handles decision-making and generates responses—whether it’s a text message, a soothing voice prompt, or even a reciprocal touch gesture (hello, robot hugs).
🔸 Integration Layer This layer brings all the technology and research areas together, combining perception, cognition, and response into real-world applications. Potential application areas are Emotional AI, companion AI, healthcare robots, immersive AR/VR, or any system where touch can create deeper, more human-like interactions.
This framework is designed as a guide for exploring relevant topics, determining current technologies we can leverage, identifying existing challenges and making novel contributions to address them. It also aims to promote touch as a modality in AI and robotics, encouraging more developers and researchers to start exploring and contributing to this exciting field.
Why It Matters
As AI steps out from behind screens into our homes, workplace, and public spaces, the ability to sense, understand and respond to touch is an essential step towards emotional intelligence. We’re moving toward a future where AI isn’t just intelligent at performing tasks, but also intelligent in emotional and social situations. And physical interaction becomes increasingly important as it starts to take physical form.